
Microsoft Office 365’s Data Recovery Options
By Jared MatfessJared is a Technology Practice Leader working for Slalom Consulting, a Microsoft Managed Partner providing national Business & IT solutions headquartered in Seattle, Washington. He is a Microsoft Certified Professional (MCP), and has over a decade of experience building technical solutions, and solving business problems. He is a regular speaker at user groups and SharePoint Saturdays all up and down the East Coast. Jared is also a Microsoft Most Valuable Professional (MVP) in the Office Servers and Services category. He can be reached through his blog or on Twitter (@jaredmatfess).
As businesses continue to move more of their critical workloads to Office 365, the need to evaluate procedures for “what if” scenarios become even more important. The nature of Office 365 is that you rely on Microsoft to provide you with a service that is highly available across multiple data centers, however it is important to be aware of what options exist for events where data is lost, the most common being user error.
In the event of data loss via accidental deletion, here is an overview of the recovery options for some of Office 365’s most popular services.
SharePoint Online Recovery and Data Retention
Site Collections – Site Collections are kept in the tenant recycle bin and can be restored within 30 days of deletion through the Office 365 Admin Center or through executing the Restore-SPDeletedSite command from PowerShell.
To see a list of deleted site collections you would connect to SharePoint Online via PowerShell and then you can type in Get-SPODeletedSite. This will return a list of all your deleted site collections along with when it was deleted, the storage quota, and how many days are remaining before it is permanently deleted from your tenant.
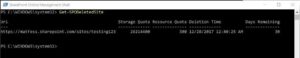
To restore a deleted site collection you would type the command:
Restore-SPODeletedSite -Identity https://matfess.sharepoint.com…
The site collection will be available once the command has finished running along with all data that was previously in that site collection, including any items that were in the recycle bins.
Items – all objects consisting of documents, list items, subsites, lists, libraries, etc. are retained for 93 days from the time you delete them from their original location. Users can restore items from within their personal recycle bin along with any applicable metadata. Not that when data is deleted, you will have 93 days to recover in SharePoint Online period. If users empty their personal recycle bin, the items will be moved to the Second-Stage Recycle Bin which a Site Collection Administrator can access, unless the 93 day mark has expired.
OneDrive for Business Recovery and Data Retention
Files – OneDrive for Business has the same 93 day retention period for deleted items – the only difference is that a user is considered a Site Collection Administrator for their personal site. Therefore, the Recycle Bin they access through the user interface is essentially the Second-Stage Site Collection recycle bin.
There is also a new feature on the Office 365 Roadmap that was announced at Microsoft Ignite called “Files Restore.” Based on the overview it would appear that this feature would allow users to restore a “snapshot” of their OneDrive in the event of a catastrophic event, however it’s still unclear as to the granularity of the restore, how far back historical snapshots will go, structure retention, whether restores are destructive or not, and what licenses will be allowed this feature. Without a set date on this release and limited insight into what can be recovered, a backup solution still needs to be in place for OneDrive files.
Office 365 Administrators should pay attention to this feature as it rolls out sometime in 2018, but be aware that should Microsoft’s systems go down or an error occur on their side, your data will be compromised with this feature. Best practices state that your backup data should exist in a location independent of the app itself. That way, if primary and local backup data were destroyed, you’d have another copy offsite to restore from. This is Disaster Recovery 101, but for some reason many overlook this when it comes to SaaS data. This is a big mistake. Your OneDrive data is just as susceptible to data loss without an offsite copy of your data.
Exchange Online Recovery and Data Retention
User Mailboxes – user mailboxes are retained for 30 days post deletion, and can be restored by restoring the corresponding user account in the Office 365 admin center. In the event that the 30 day retention period has passed, know that this data will likely be purged from Microsoft. Also, know the difference between a hard and soft delete in Exchange that may not afford you the 30 day retention period.
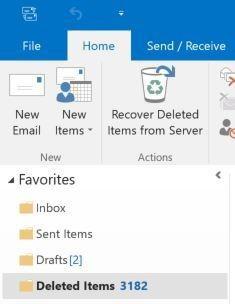
Messages – depending on any custom retention periods you configure within your tenant, users can find deleted messages within their Deleted Items folder in both the Outlook Client as well as Outlook Web Access. If the message is no longer in the Deleted Items folder due to a user permanently deleting it or through a retention policy (learn how to configure deleted item retention and recoverable items quotas), it still might be possible to recover the message through “Recover Deleted Items from Server” functionality within the Outlook client if it has been less than 14 days from when it was purged from the Deleted Items folder.
To attempt recovering a deleted message, you should select the Deleted Items folder in your Outlook Client, and then select “Recover Deleted Items from Server” from the ribbon.
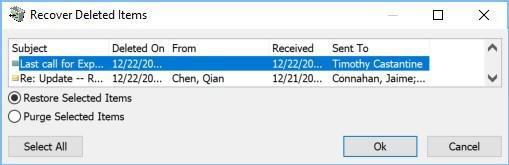
From there you can highlight the message which you would like to recover, ensure the Restore Selected Items radio is selected, and click the Ok button. Data will only be available for recovery with the “Recover Deleted Items from Storage” option for 14 days.
Conclusion
While there is a common theme across the various Office 365 services where you are able to restore items as long as you meet Microsoft’s or your own organization’s retention policies, admins need to be ready in the event of the worst-case scenario.
In addition, Microsoft’s data retention options are purely focused on the deletion of items versus the integrity of the data. In reality, the Office 365 service provides you with high availability access to your files, but does not account for events where data becomes corrupted. This is where you might want to consider a 3rd party SaaS backup solution for Office 365 that can help you recover your data back to a non-corrupted state.
Ensuring that your data is recoverable – and recoverable quickly and easily – should be at the top of your to-do list this year. The native functionality within Office 365 above has limits, and the only surefire way you can protect your Office 365 data against any number of the most common causes of data loss is by having an independent backup solution in place. To get a guided demo of Backupify today, click here.